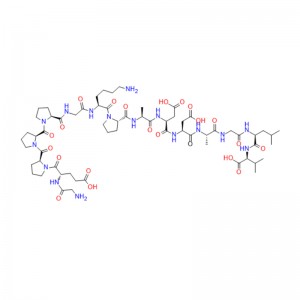
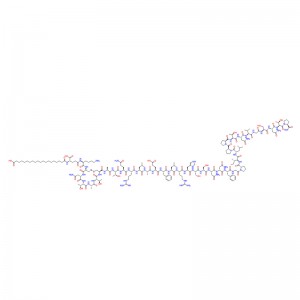
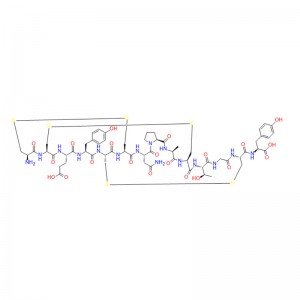
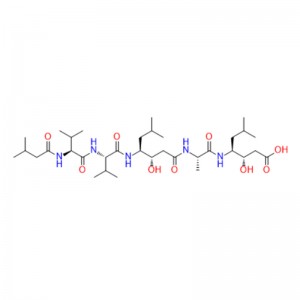
In human gastric juice, BPC 157 is stable for more than 24 hours, and thus it has good oral bioavailability (always given alone) and beneficial effects in the entire gastrointestinal tract . This is an important distinction from the otherstandard peptides, which are functionally dependent on theaddition of carrier or are otherwiserapidly destroyed in human gastric juice.Consequently, stable BPC 157 is suggested to be a mediator of Robert’s cytoprotection, which maintains the integrity ogastrointestinal mucosa. We suggest that the contribution of BPC 157 to Robert’s cytoprotection – that is, the ability to counteract fundamental alcohol-induced gastric lesions, which Robert called cytoprotection – and the ability to counteract lesions arising from the direct injurious contact of the noxious agent with the cell represent the peripheral connection between the gut and the brain axis.
Perovic reported that BPC 157 has a marked therapeutic effect pertaining to the recovery of rats with a spinal cord injury with tail paralysis (1-minute compression injury of the sacrocaudal spinal cord [S2–Co1]). Specifically, a single intraperitoneal BPC 157 administration at 10 minutes post-injury counteracts the negative effects. By contrast, the spinal cord injury and tail paralysis persist in untreated rats, assessed days, weeks, months, and a year after the injury. Of note, BPC 157 attenuates the commonly caused damage . Thereby, BPC 157 therapy results in evident functional, microscopic, and electrophysiologic recovery .



Of note, in rats with spinal cord injury, there is permanent reperfusion. Once BPC 157 is administered 10 minutes post-compression injury, there is continuous protection and no spontaneous spinal cord injury-induced disturbances reappear.All spinal cord injuries immediately provoke hemorrhage, with subsequent death of neurons and oligodendrocytes.
Hence, it is conceivable that early hemostasis may be beneficial and enable functional recoveryafter spinal cord contusion in rats. However, the effect exerted by BPC 157 is likely different from the simple hemostatic effect that would attenuate spinal cord injury, because BPC 157 also markedly improves thrombocyte function in rats without affecting coagulation factors. During recovery from spinal cord injury, BPC 157 also directly protects the endothelium, alleviates peripheral vascular occlusion disturbances, rapidly activates alternative bypass pathways, and counteracts venous occlusion–induced syndromes. Thus, assuming that there is a substantial venous contribution to the spinal cord compression, it is conceivable that the reestablished blood flow mediated by BPC 157 may undoubtedly contribute to the rapid recovery effect. Furthermore, considering that BPC 157 promotes permanent reperfusion after spinal cord compression, it should be noted that when BPC 157 is given during reperfusion, it counteracts stroke induced by bilateral clamping of the common carotid arteries. BPC 157 resolves neuronal damage and prevents memory, locomotor, and coordination deficits. BPC 157 apparently exerts these effects by altering gene expression in the hippocampus .
In conclusion, BPC 157 exerts beneficial effects on stroke, schizophrenia, and spinal cord injury .
Researchers have consistently demonstrated that BPC 157 exerts a myriad of beneficial effects throughout the body. There is no reason to indicate that the benefits of BPC 157 are limited by the validity of the utilized models and/or methodology limitations. Indeed, we can argue that the effectiveness, easy applicability, safe clinical profile and mechanism of BPC 157 represent an alternative, likely successful, future therapeutic direction for neurological conditions. Therefore, additional studies are needed to clarify how potential BPC 157 therapy would specifically deal with a mechanism of action that involves multiple subcellular sites in the CNS. The influence on the function of most, if not all, neuronal systems at the molecular, cellular, and systemic levels should be explored. Some visceral repetitive relay of the CNS or circumventricular organs, one of the few regions in the brain without the blood-brain barrier, is a known pathway by which a systemically administered peptide can exert a central effect. Thus, it must act within the gut-brain axis, regardless of whether this action is direct or indirect.